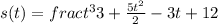Answer:
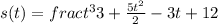
Explanation:
Relation between acceleration, velocity and position:
The velocity function is the integral of the acceleration function.
The position function is the integral of the velocity function.
Acceleration:
As given by the problem, the acceleration function is
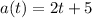
Velocity:
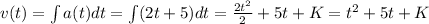
In which K is the constant of integration, which is the initial velocity. So K = -3 and:
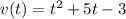
Position:
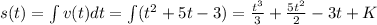
In which K, the constant of integration, is the initial position. Since it is 12: