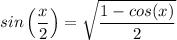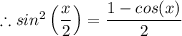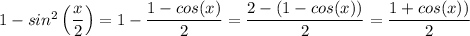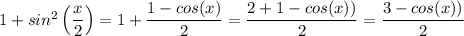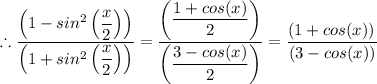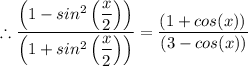Answer:
Given that we have;
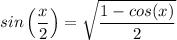
By the application of the law of indices and algebraic process of adding a and subtracting a fraction from a whole number, we have;
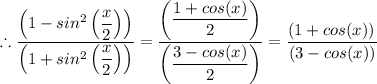
Explanation:
An identity is a valid or true equation for all variable values
The given equation is presented as follows;
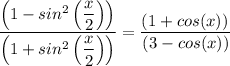
From trigonometric identities, we have;