Given:
P(x) is a 2nd degree polynomial.
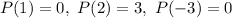
To find:
The polynomial P(x).
Solution:
If P(x) is a polynomial and P(c)=0, then c is a zero of the polynomial and (x-c) is a factor of polynomial P(x).
We have,
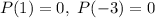 . It means 1 and -3 are two zeros of the polynomial P(x) and (x-1) and (x+3) are two factors of the polynomial P(x).
. It means 1 and -3 are two zeros of the polynomial P(x) and (x-1) and (x+3) are two factors of the polynomial P(x).
So, the required polynomial is defined as:
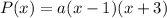 ...(i)
...(i)
Where, a is a constant.
We have,
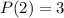 . So, substituting
. So, substituting
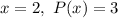 in (i), we get
in (i), we get
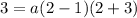
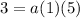
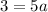
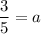
Putting
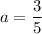 in (i), we get
in (i), we get
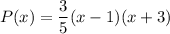
Therefore, the required polynomial is
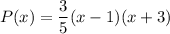 .
.