Answer:
Radius of Convergence: 2
Interval of Convergence: [-2, 2]
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Equality Properties
- Multiplication Property of Equality
- Division Property of Equality
- Addition Property of Equality
- Subtraction Property of Equality
Algebra I
- Exponential Rule [Multiplying]:
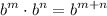
- Exponential Rule [Dividing]:
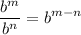
Calculus
Series Convergence Tests
- P-Series:
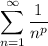
- Direct Comparison Test (DCT)
- Alternating Series Test (AST)
- Ratio Test:
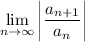
Radius of Convergence (ROC)
Interval of Convergence (IOC)
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
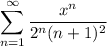
Step 2: Find ROC
Apply Ratio Test
- [Series] Set up [Ratio Test]:
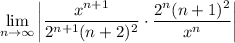
- [Ratio Test] Rewrite exponentials [Exponential Rule - Multiplying]:
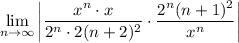
- [Ratio Test] Simplify:
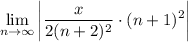
- [Ratio Test] Multiply:
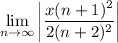
- [Ratio Test] Evaluate limit:
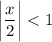
- [Ratio Test] Isolate x:
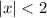
Our ROC is 2.
Step 3: Find IOC
Test endpoints
- [ROC] Find interval bound:
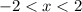
x = -2
- Substitute in x [Series]:
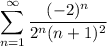
- [Series] Rewrite [Exponential Rules - Multiplying]:
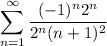
- [Series] Simplify:
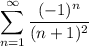
Test convergence of modified series: Alternating Series Test
- [AST] Condition 1 [Limit Test]:
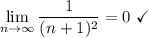
- [AST] Condition 2 [aₙ vs bₙ comparison]:
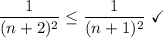
At x = -2, the series is convergent.
∴ Current IOC is -2 ≤ x < 2 or [-2, 2); 2 undetermined
x = 2
- Substitute in x [Series]:
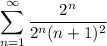
- [Series] Simplify:
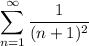
Test convergence of modified series: Direct Comparison Test
- [DCT] Condition 1 [Define comparing series]:
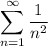
- [DCT] Condition 1 [Test convergence of comparing series]:
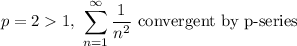
- [DCT] Condition 2 [aₙ vs bₙ comparison]:
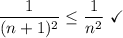
At x = 2, the series is convergent.
∴ IOC for
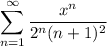 is -2 ≤ x ≤ 2 or [-2, 2]
is -2 ≤ x ≤ 2 or [-2, 2]
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/II)
Unit: Taylor Polynomials and Approximations - Power Series (BC Only)
Book: College Calculus 10e