Answer:
4.06 mol H₂O
Step-by-step explanation:
- 2C₆H₁₄ + 19O₂ → 12CO₂ + 14H₂O
First we convert the given masses of reactants into moles, using their respective molar masses:
- 250 g O₂ ÷ 32 g/mol = 7.81 mol O₂
- 50 g C₆H₁₄ ÷ 86 g/mol = 0.58 mol C₆H₁₄
Now we calculate how many O₂ moles would react completely with 0.58 C₆H₁₄ moles, using the stoichiometric coefficients of the reaction:
- 0.58 mol C₆H₁₄ *
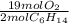 = 5.51 mol O₂
= 5.51 mol O₂
As there are more O₂ moles than required (7.81 vs 5.51), O₂ is the reactant in excess. That means that C₆H₁₄ is the limiting reactant.
Now we can calculate how much water can be formed, using the number of moles of the limiting reactant:
- 0.58 mol C₆H₁₄ *
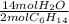 = 4.06 mol H₂O
= 4.06 mol H₂O