Answer:
NBr₃ is the excess reactant.
Step-by-step explanation:
- 2NBr₃ + 3NaOH → N₂ + 3NaBr + 3HOBr
We can solve this problem by calculating how many moles of NaOH would react completely with 40 moles of NBr₃, using the stoichiometric coefficients of the reaction:
- 40 mol NBr₃ *
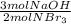 =60 moles NaOH
=60 moles NaOH
As the required number of NaOH moles is higher than the available number (60 required vs 48 available), NaOH is the limiting reactant.
As such, the excess reactant is NBr₃.