Answer: The pressure is 1137.5 mm Hg its pressure if its volume is increased to 150
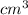 at 35 °C
at 35 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
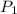 = 750 mm Hg,
= 750 mm Hg,
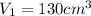 ,
,
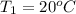
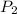 = ?,
= ?,
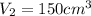 ,
,
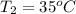
Formula used to calculate the new pressure is as follows.
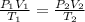
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
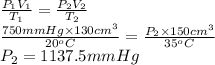
Thus, we can conclude that the pressure is 1137.5 mm Hg its pressure if its volume is increased to 150
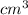 at 35 °C.
at 35 °C.