Given :
A sample of gas occupies 200 L at 780 mm Hg and 280 K.
To Find :
The new volume, in liters, of the gas at 810 mm Hg and 300 K.
Solution :
We know, by ideal gas equation :
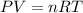
Since, every thing is constant except
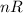 .
.
So,
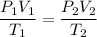
Putting all given values we get :
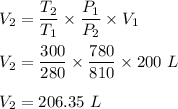
Therefore, the new volume is 206.35 L.