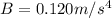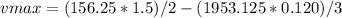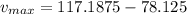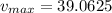Answer:
(a)
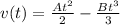 --- velocity
--- velocity
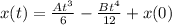 --- position
--- position
(b) The maximum velocity is: 39.0625m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
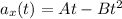
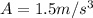
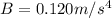
Solving (a): The position and velocity as a function
To calculate the change in velocity, we integrate the given acceleration
i.e.
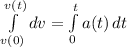
Integrate
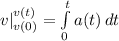
Substitute v(t) and v(0) for v
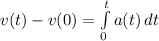
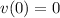 ---- The initial velocity.
---- The initial velocity.
So, we have:
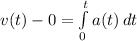
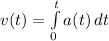
Substitute:
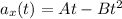
![v(t) = \int\limits^t_0 {[At -Bt^2]} \, dt](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/vdx57ai5pmm2jc2t8qym3bacixfh34lq5g.png)
Integrate
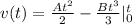
Substitute 0 and t for t
![v(t) = [(At^2)/(2) -(Bt^3)/(3)] - [(A*0^2)/(2) -(B*0^3)/(3)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/25xngwn0z2fl5uwioyp9k6hzng1xjqq0fi.png)
![v(t) = [(At^2)/(2) -(Bt^3)/(3)] - 0](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/tzu3kmni1vh5g0vp5sechqsvyks4mt7koq.png)
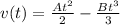
To calculate the change in position, we integrate the calculated velocity
i.e.
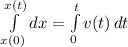
Integrate
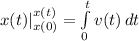
Substitute x(t) and x(0) for x(t)
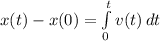
Substitute:
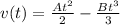
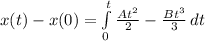
Integrate
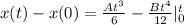
Substitute t and 0 for t
![x(t) - x(0) = [(At^3)/(6) -(Bt^4)/(12)] - [(A*0^3)/(6) -(B*0^4)/(12)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/1r0q1t9glnvzhcih6c20ipo20y5ltt822a.png)
![x(t) - x(0) = [(At^3)/(6) -(Bt^4)/(12)] - [0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/high-school/jxsow5o3c5q066bbehgxjhm55es329pjkn.png)
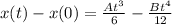
Make x(t) the subject
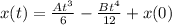
Where x(0) represents the initial position
Solving (b): The maximum velocity
First, we calculate the time at which it attains the maximum height
Set acceleration to 0
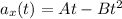
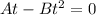
Factorize
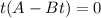
Split
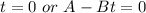
t can't be 0.
So, we have:
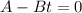
Solve for t
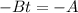
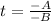
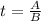
Substitute:
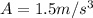 and
and
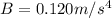
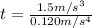
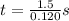
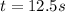
Substitute
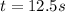 in v(t) to get the maximum velocity
in v(t) to get the maximum velocity
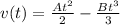
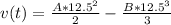
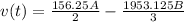
Substitute:
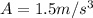 and
and