Answer:
c. Equal to the magnitude of the average velocity for the same time period if the direction of motion does not change.
Step-by-step explanation:
Speed can be defined as distance covered per unit time. Speed is a scalar quantity and as such it has magnitude but no direction.
Mathematically, speed is given by the equation;
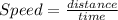
Motion can be defined as a change in the location (position) of a physical object or body with respect to a reference point.
This ultimately implies that, motion would occur as a result of a change in location (position) of an object with respect to a reference point or frame of reference i.e where it was standing before the effect of an external force.
The average speed of an object during a specified period of time is equal to the magnitude of the average velocity traveled or covered in the same time period and in a straight line i.e if the direction of motion does not change.