Answer:
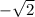 and
and
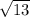
Explanation:
Given a polynomial with rational coefficients, its irrational and complex roots would occur in conjugate pairs.
For example, if the roots of a polynomial are 2 +
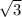 , 3 and 4 - 3i, then 2 -
, 3 and 4 - 3i, then 2 -
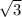 , and 4 + 3i are also roots of the polynomial.
, and 4 + 3i are also roots of the polynomial.
Therefore, since the given polynomial has rational coefficients and some of its roots are ,
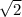 and -
and -
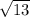 , then -
, then -
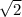 and
and
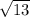 are also roots of the polynomial.
are also roots of the polynomial.