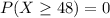Answer:
a)
In this question, for each call, there are only two possible outcomes, either it is successful, or it is not, so binary outcomes. For each call, the probability of a success or failure is the same, which means that the trials are independent, having the same value of p. And the number of trials, which is 50, is fixed. This means that this is a binomial distribution.
b) The mean is 1 and the standard deviation is 0.9899.
c)
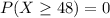
Explanation:
Binomial probability distribution
The binomial probability is the probability of exactly x successes on n repeated trials, and X can only have two outcomes.
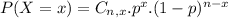
In which
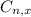 is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
is the number of different combinations of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
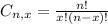
And p is the probability of X happening.
The expected value of the binomial distribution is:
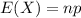
The standard deviation of the binomial distribution is:
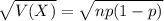
From past experience, she is successful on 2% of her calls.
This means that
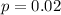
50 calls.
This means that

a. This is binomial distribution. Explain using the BINS method why this is so.
BINS: Binary outcomes, Independent Trials, n is fixed, and same value of p for all trials.
In this question, for each call, there are only two possible outcomes, either it is successful, or it is not, so binary outcomes. For each call, the probability of a success or failure is the same, which means that the trials are independent, having the same value of p. And the number of trials, which is 50, is fixed. This means that this is a binomial distribution.
b. Find the mean and standard deviation of X.
The mean is:
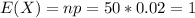
The standard deviation is:
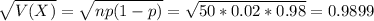
The mean is 1 and the standard deviation is 0.9899.
c. Find the probablity of P(X>or equal to 48)
This is:
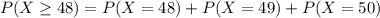
In which
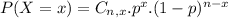
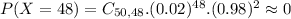
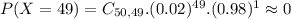
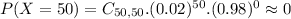
So