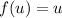Answer:
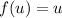
Explanation:
Given
![\int {\ln(u)} \, du = u[\ln(u) - f(u)] + c](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/3uvwv3kgsdhof62e3wxd76fa4txhcvs9wh.png)
Required
Find f(u)
To do this, we start by integrating the left-hand side
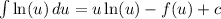
Using integration by parts, we have:
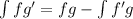
So, we have:
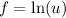
Differentiate
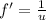
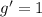
Integrate
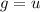
So:
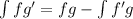
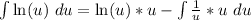
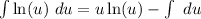
So, we have:
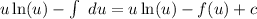
Integrate du using constant rule
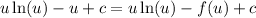
Subtract c from both sides
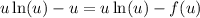
Subtract u ln(u) from both sides
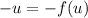
Rewrite as: