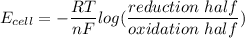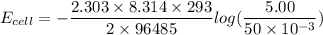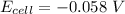Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
For a certain metal M by which the electrodes and the solution M_2SO_4 the cell notation is:
SALT BRIDGE
ANODE ↓ CATHODE
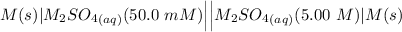
Since the standard electrode potential is less positive on the left side, a negative anode electrode is used, and oxidation occurs at the anode.
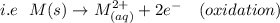
The right side of the cell cathode is placed which is positive in sign and aids in reduction since the normal reduction potential is less negative.
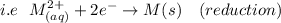
As a result, the correct answer for the positive electrode is the right side.
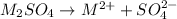
Using Nernst Equation: