Solution :
Given :
M = 0.35 kg

Total mechanical energy = constant
or
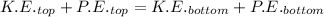
But
 and
and
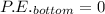
Therefore, potential energy at the top = kinetic energy at the bottom

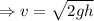
 (h = 35 cm = 0.35 m)
(h = 35 cm = 0.35 m)
= 2.62 m/s
It is the velocity of M just before collision of 'm' at the bottom.
We know that in elastic collision velocity after collision is given by :
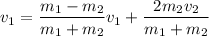
here,
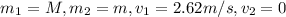
∴


= 0.33 m/s
Therefore, velocity after the collision of mass M = 0.33 m/s