Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the given information;
The chemical reaction can be well presented as follows:
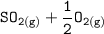 ⇄
⇄
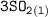
Now, K is known to be the equilibrium constant and it can be represented in terms of each constituent activity:
i.e
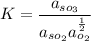
However, since we are dealing with liquids solutions;
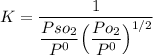 since the activity of
since the activity of
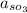 is equivalent to 1
is equivalent to 1
Hence, under standard conditions(i.e at a pressure of 1 bar)
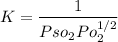
(b)
From the CRC Handbook, we are meant to determine the value of the Gibb free energy by applying the formula:
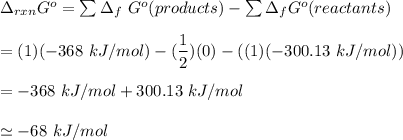
Thus, for this reaction; the Gibbs frree energy = -68 kJ/mol
(c)
Le's recall that:
At equilibrium, the instantaneous free energy is usually zero &
Q(reaction quotient) is equivalent to K(equilibrium constant)
So;
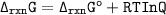

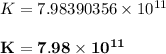
(d)
The direction by which the reaction will proceed can be determined if we can know the value of Q(reaction quotient).
This is because;
If Q < K, then the reaction will proceed in the right direction towards the products.
However, if Q > K , then the reaction goes to the left direction. i.e to the reactants.
So;
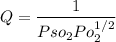
Since we are dealing with liquids;
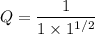
Q = 1
Since Q < K; Then, the reaction proceeds in the right direction.
Hence, SO2 as well O2 will combine to yield SO3, then condensation will take place to form liquid.