Answer:
0.0588 = 5.88% probability that a middle-aged man with diabetes is very active
Explanation:
Conditional Probability
We use the conditional probability formula to solve this question. It is
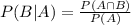
In which
P(B|A) is the probability of event B happening, given that A happened.
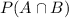 is the probability of both A and B happening.
is the probability of both A and B happening.
P(A) is the probability of A happening.
In this question:
Event A: Has diabetes.
Event B: Is very active.
Probability of having diabetes:
To find this probability, we take in consideration that:
It also found that men who were very active (burning about 3,500 calories daily) were a fourth as likely to develop diabetes compared with men who were sedentary. Assume that one-fifth of all middle-aged men are very active, and the rest are classified as sedentary.
So the probability of developing diabetes is:
x of 4/5 = x of 0.8(not active)
x/4 = 0.25x of 1/5 = 0.2(very active). So
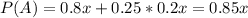
Probability of developing diabetes while being very active:
0.25x of 0.2. So
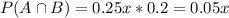
What is the probability that a middle-aged man with diabetes is very active?
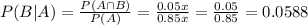
0.0588 = 5.88% probability that a middle-aged man with diabetes is very active