Answer:
1: At temperatures below 542.55 K
2: At temperatures above 660 K
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the thermodynamic definition of the Gibbs free energy, it is possible to write the following expression:
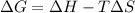
Whereas ΔG=0 for the spontaneous transition. In such a way, we proceed as follows:
1:
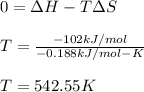
It means that at temperatures lower than 542.55 K the reaction will be spontaneous.
2:
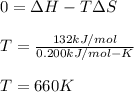
It means that at temperatures higher than 660 K the reaction will be spontaneous.
Best regards!