Answer:
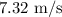
Step-by-step explanation:
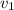 = Velocity at initial point = 0
= Velocity at initial point = 0
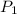 = Pressure in tank = 120 kPa
= Pressure in tank = 120 kPa
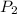 = Pressure at outlet = 101 kPa
= Pressure at outlet = 101 kPa
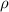 = Density of kerosene =
= Density of kerosene =
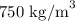
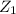 = Tank height = 15 cm
= Tank height = 15 cm
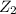 = Height of pipe exit = 0
= Height of pipe exit = 0
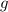 = Acceleration due to gravity =
= Acceleration due to gravity =
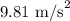
From Bernoulli's equation we have
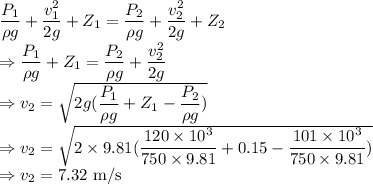
The exit velocity from the tube is
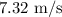 .
.