Given:
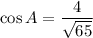
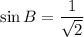
A and B both lies in I quadrant.
To find:
The value of
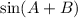 .
.
Solution:
We know that, all trigonometric ratios are positive in first quadrant.
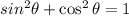
Using this we get
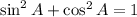
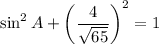
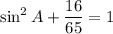
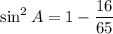
Taking square root on both sides, we get
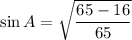 [Only positive because A lies in I quadrant]
[Only positive because A lies in I quadrant]
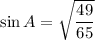
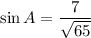
Similarly,
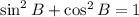
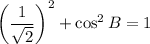
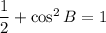
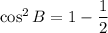
Taking square root on both sides, we get
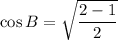 [Only positive because B lies in I quadrant]
[Only positive because B lies in I quadrant]
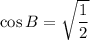
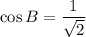
Now,
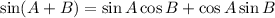
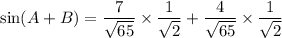
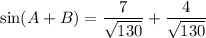
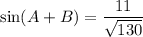
Therefore, the exact value of
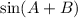 is
is
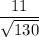 .
.