Answer:
The 90% confidence interval for the difference between the proportions of Democrats and Republicans who approve of the mayor's performance is (-0.1078, 0.1702).
Explanation:
Before building the confidence interval, we need to understand the central limit theorem and subtraction of normal variables.
Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem estabilishes that, for a normally distributed random variable X, with mean
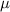 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
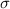 , the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
, the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
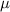 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
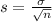 .
.
For a skewed variable, the Central Limit Theorem can also be applied, as long as n is at least 30.
For a proportion p in a sample of size n, the sampling distribution of the sample proportion will be approximately normal with mean
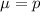 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
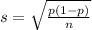
Subtraction of normal variables:
When two normal variables are subtracted, the mean is the subtraction of the means while the standard deviation is the square root of the sum of the variances.
In a random sample of 42 Democrats from one city, 10 approved of the mayor's performance.
This means that:
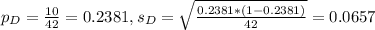
In a random sample of 58 Republicans from the city, 12 approved of the mayor's performance.
This means that:
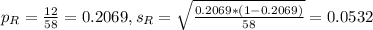
Distribution of the difference:
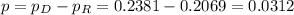
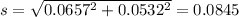
Confidence interval:
We have that to find our
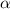 level, that is the subtraction of 1 by the confidence interval divided by 2. So:
level, that is the subtraction of 1 by the confidence interval divided by 2. So:
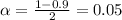
Now, we have to find z in the Ztable as such z has a pvalue of
 .
.
That is z with a pvalue of
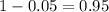 , so Z = 1.645.
, so Z = 1.645.
Now, find the margin of error M as such
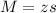
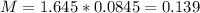
The lower end of the interval is the sample mean subtracted by M. So it is 0.0312 - 0.139 = -0.1078
The upper end of the interval is the sample mean added to M. So it is 0.0312 + 0.139 = 0.1702
The 90% confidence interval for the difference between the proportions of Democrats and Republicans who approve of the mayor's performance is (-0.1078, 0.1702).