Step-by-step explanation:
Before we start with any calculation, we need to determine the stoichiometric relationship between the reactants consumed and the products formed. In other words, we need to establish a balanced chemical equation that describes the decomposition of calcium carbonate as shown below.
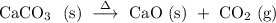 ,
,
where the uppercase delta symbol,
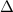 , above the chemical reaction arrow denotes that heat is applied to make the reaction proceed in the direction of the arrow.
, above the chemical reaction arrow denotes that heat is applied to make the reaction proceed in the direction of the arrow.
To calculate how many moles are there in 4 grams of calcium carbonate, we use the relation
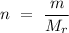 ,
,
where
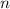 is the number of moles,
is the number of moles,
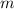 is the mass of the chemical substance and
is the mass of the chemical substance and
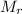 is the molar mass of the chemical substance. We first need to identify the molar mass of calcium carbonate,
is the molar mass of the chemical substance. We first need to identify the molar mass of calcium carbonate,
![M_(r) \, [\text{CaCO}_(3)] \ = \ A_(r) \, [\text{Ca}] \ + \ A_(r) \, [\text{C}] \ + \ 3 \, * \, A_(r) \, [\text{O}] \\ \\ M_(r) \, [\text{CaCO}_(3)] \ = \ 40.078 \ + \ 12.011 \ + \ 3 \, * \, 15.999 \\ \\ M_(r) \, [\text{CaCO}_(3)] \ = \ 100.086 \ \text{g mol}^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/high-school/97urlmy76zmadqtsbais9sudftmshyp8kz.png)
Hence,
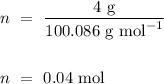 .
.
We know that, from the balanced chemical equation above, 1 mole of calcium carbonate following decomposition, will theoretically lead to the production of 1 mole of carbon dioxide. Then, if 0.04 moles of calcium carbonate is decomposed, then, 0.04 moles of carbon dioxide is produced.
To convert the number of moles into the mass of carbon dioxide produced, we need to rearrange the formula as follows.
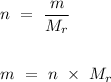 .
.
Thus,
![M_(r) \, [\text{CO}_(2)] \ = \ A_(r) \, [\text{C}] \ + \ 2 \, * \, A_(r) \, [\text{O}] \\ \\ M_(r) \, [\text{CO}_(2)] \ = \ (12.011 \ + \ 2 \, * \, 15.999) \ \text{g mol}^(-1) \\ \\ M_(r) \, [\text{CO}_(2)] \ = \ 44.009 \ \text{g mol}^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hcvyxhhcpvmzx6rgiayjk8dn763k51086w.png)

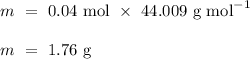
Therefore, 4 grams of calcium carbonate yields 1.76 grams of carbon dioxide following decomposition.