Answer:
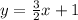
Explanation:
What we need to know:
- Linear equations are typically organized in slope-intercept form:
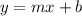 where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept (the value of y when the line crosses the y-axis)
where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept (the value of y when the line crosses the y-axis) - Parallel lines always have the same slope (m) and different y-intercepts (b)
1) Find the slope of line P
The slope of a line is equal to the
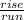 , or the number of units the line moves up over the number of units the line moves to the right.
, or the number of units the line moves up over the number of units the line moves to the right.
We can see that for line P, for every 2 units it moves to the right, it moves up 3 units.
Therefore, the slope of line P is
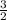 .
.
Knowing this, the equation of a line parallel to line P would have a slope of
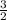 as well. Plug this into
as well. Plug this into
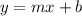 as m:
as m:
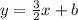
2) Plug the given point Q into
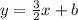 to find the y-intercept (b)
to find the y-intercept (b)
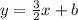
Plug in point Q (2,4)
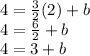
Subtract 3 from both sides
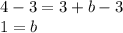
Therefore, the y-intercept of this line (b) is 1. Plug this back into our original equation:
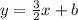
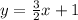
I hope this helps!