Answer: The value of
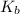 for chloroform is
for chloroform is
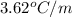 when 0.793 moles of solute in 0.758 kg changes the boiling point by 3.80 °C.
when 0.793 moles of solute in 0.758 kg changes the boiling point by 3.80 °C.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given: Moles of solute = 0.793 mol
Mass of solvent = 0.758
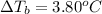
As molality is the number of moles of solute present in kg of solvent. Hence, molality of given solution is calculated as follows.
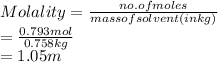
Now, the values of
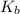 is calculated as follows.
is calculated as follows.
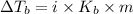
where,
i = Van't Hoff factor = 1 (for chloroform)
m = molality
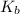 = molal boiling point elevation constant
= molal boiling point elevation constant
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
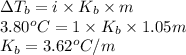
Thus, we can conclude that the value of
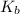 for chloroform is
for chloroform is
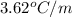 when 0.793 moles of solute in 0.758 kg changes the boiling point by 3.80 °C.
when 0.793 moles of solute in 0.758 kg changes the boiling point by 3.80 °C.