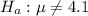Answer:
The null hypothesis is
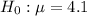
The alternate hypothesis is
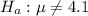
Explanation:
The diameter of a spindle in a small motor is supposed to be 4.1 millimeters
This means that the null hypothesis is that the diameter has the supposed value, that is,
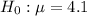
If the spindle is either too small or too large, the motor will not work properly. The manufacturer measures the diameter in a sample of 41 spindles to determine whether the mean diameter has moved away from the required measurement.
Tests if it has moved away, that is, if the mean is different from the specified value of 4.1. So the alternate hypothesis is