Answer:
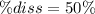
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, when considering weak acids which have an associated percent dissociation, we first need to set up the ionization reaction and the equilibrium expression:
![HA\rightleftharpoons H^++A^-\\\\Ka=([H^+][A^-])/([HA])](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/kgnp09m0exh9jwka74bdbzzic26jxtrupb.png)
Now, by introducing x as the reaction extent which also represents the concentration of both H+ and A-, we have:
![Ka=(x^2)/([HA]_0-x) =10^(-4.74)=1.82x10^(-5)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/orfdrjuign0x0pqk52bh7xphfxchevrpxd.png)
Thus, it is possible to find x given the pH as shown below:
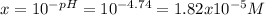
So that we can calculate the initial concentration of the acid:
![((1.82x10^(-5))^2)/([HA]_0-1.82x10^(-5)) =1.82x10^(-5)\\\\(1.82x10^(-5))/([HA]_0-1.82x10^(-5)) =1\\\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/93dhwn606d71t2d6vgu6qsa8c1nexx3y5g.png)
![[HA]_0=3.64x10^(-5)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/y05qmnker8jd052s97hkwilgsty6jdvkg1.png)
Therefore, the percent dissociation turns out to be:
![\% diss=(x)/([HA]_0)*100\% \\\\\% diss=(1.82x10^(-5)M)/(3.64x10^(-5)M)*100\% \\\\\% diss = 50\%](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/high-school/xytbh4j6pk00dfi1j6kdy2cztg0cz015es.png)
Best regards!