Answer: If
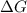 for a reaction equals zero, the reaction is at equilibrium.
for a reaction equals zero, the reaction is at equilibrium.
Step-by-step explanation:
When a thermodynamic closed system tends to do the maximum amount of non-expansion work then the energy used to do this work is called Gibb's free energy.
The expression for
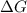 can be written as follows.
can be written as follows.
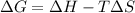
where,
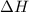 = enthalpy change
= enthalpy change
T = temperature
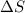 = entropy change
= entropy change
This means that
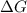 is the difference between heat released in a process and the amount of heat released in a reversible manner for the same process. So, when the value of of
is the difference between heat released in a process and the amount of heat released in a reversible manner for the same process. So, when the value of of
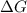 comes out to be equal to zero then it means no heat is released or absorbed.
comes out to be equal to zero then it means no heat is released or absorbed.
Hence, the reaction is stable or at equilibrium.
Thus, we can conclude that the value of
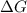 = 0 then it means that the reaction is at equilibrium.
= 0 then it means that the reaction is at equilibrium.