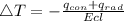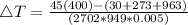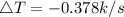Answer:
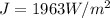
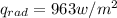
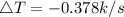
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that:
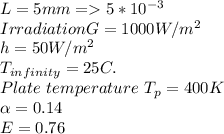
at Temp=400K
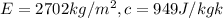
Generally the equation for Radiosity is mathematically given by
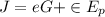
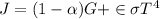
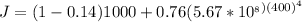
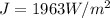
Generally the equation for net radiation heat flux
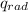 is mathematically given by
is mathematically given by
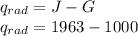
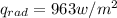
Generally the equation for and the rate of plate temp
 is mathematically given by
is mathematically given by