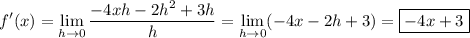Using the limit definition of the derivative, you have
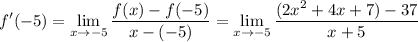
Simplify the numerator:
(2x ² + 4x + 7) - 37 = 2x ² + 4x - 30
… = 2 (x ² + 2x - 15)
… = 2 (x + 5) (x - 3)
Then
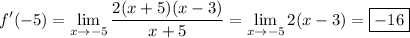
• • •
For your second question in the comments, if f(x) = -2x ² + 3x - 7, then by the definition of the derivative, you have
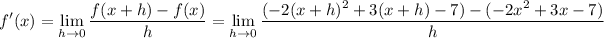
Simplify the numerator:
(-2 (x + h)² + 3 (x + h) - 7) - (-2x ² + 3x - 7)
… = (-2x ² - 4xh - 2h ² + 3x + 3h - 7) - (-2x ² + 3x - 7)
… = -4xh - 2h ² + 3h
Now compute the limit: