Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The law of conservation of mass states that mass cannot be created or destroyed. The mass of the reactants must equal the mass of the products. Basically, the number of atoms at the beginning is the same as the end.
Count up the atoms on the left and right sides of the arrow. Remember to account for coefficients and subscripts.
1. 2Fe+3O₂⇒Fe₂O₃
Right: 2Fe + 3O₂
- 2 Fe atoms and 6 O atoms (3 * 2 per molecule)
Left: Fe₂O₃
- 2 Fe atoms and 3 O atoms
- NOT balanced
2. 2H₂+ O₂ ⇒ 2H₂O₂
Right: 2H₂+O₂
- 4 H atoms (2 * 2 per molecule) and 2 O atoms
Left: 2H₂O₂
- 4 H atoms and 4 O atoms (2*2 per molecule for both)
- NOT balanced
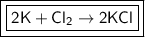
3. 2K+Cl₂⇒ 2KCl
Right: 2K + Cl₂
Left: 2KCl
- 2 K atoms and 2 Cl atoms
- This equation is balanced, but we should still check the last choice to ensure we are correct.
4. C+O₂ ⇒ 2CO
Right: C+O₂
Left: 2CO
- 2 C atoms and 2 O atoms
- NOT balanced
The only balanced equation that follows the conservation of mass is choice 3: 2K+Cl₂ ⇒2KCl