Answer:
A typical Human Cells=
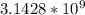 residues.
residues.
T typical Human Cells=
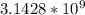 residues.
residues.
G typical Human cells=
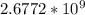 residues.
residues.
C typical Human cells=
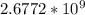 residues.
residues.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Number of human genome in pairs=2.91*10^9 base pair
Number of Human genome single bases=
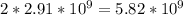 bases
bases
We know that human genome are diploid, Total Human genomes will bases will be
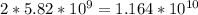 bases
bases
Since A is 27%:
A typical Human cells=
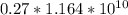
A typical Human Cells=
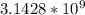 residues.
residues.
The Number of T and A residues are same in human genome. So,
T typical Human cells=
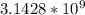 residues.
residues.
Since A and T combined form 54% of human genome then G and C form 46% combined and 23% each.
G typical Human cells=
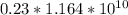
G typical Human cells=
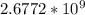 residues.
residues.
The Number of G and C residues are same in human genome. So,
C typical Human cells=
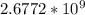 residues.
residues.