(a) If f(x) is to be a proper density function, then its integral over the given support must evaulate to 1:
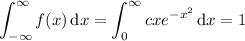
For the integral, substitute u = x ² and du = 2x dx. Then as x → 0, u → 0; as x → ∞, u → ∞:
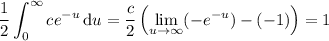
which reduces to
c / 2 (0 + 1) = 1 → c = 2
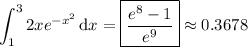
(b) Find the probability P(1 < X < 3) by integrating the density function over [1, 3] (I'll omit the steps because it's the same process as in (a)):