Answer:
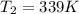
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the Charles' gas law as way to understand the volume-temperature as a directly proportional relationship for this problem, we can write:
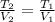
Thus, given the initial temperature and volume and the final volume, we are able to calculate the final temperature as follows:
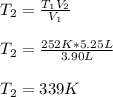
Best regards!