Answer:
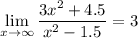
Explanation:
We want to evaluate the limit:
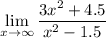
To do so, we can divide everything by x². So:
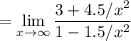
Now, we can apply direct substitution:
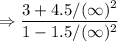
Any constant value over infinity tends towards 0. Therefore:
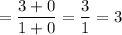
Hence:
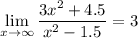
Alternatively, we can simply consider the biggest term of the numerator and the denominator. The term with the strongest influence in the numerator is 3x², and in the denominator it is x². So:
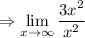
Simplify:
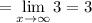
The limit of a constant is simply the constant.
We acquire the same answer.