Answer:
a. I = 30 A
b. E = 1080000 J = 1080 KJ
c. ΔT = 12.86°C
d. Cost = $ 4.32
Step-by-step explanation:
a.
The current in the coil is given by Ohm's Law:
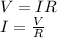
where,
I = current = ?
V = Voltage = 120 V
R = Resistance = 4 Ω
Therefore,
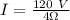
I = 30 A
b.
The energy can be calculated as:
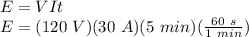
E = 1080000 J = 1080 KJ
c.
For the increase in the temperature of water:
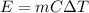
where,
m = mass of water = 20 kg
C = specific heat of water = 4.2 KJ/kg.°C
Therefore,
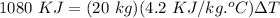
ΔT = 12.86°C
d.
First, we will calculate the total energy consumed:
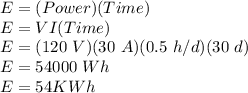
Now, for the cost:
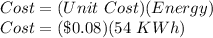
Cost = $ 4.32