Answer:

Step-by-step explanation:
We are asked to find the heat energy. Since we are given the mass, specific heat, and change in temperature, we should use this formula for heat:
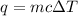
Where m is the mass, c is the specific heat, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
We know this is a 35.0 gram piece of wire, the temperature changes from 21 °C to 52°C and the specific heat is 0.900 J/ g °C.
Therefore,
- m= 35.0 g
- c= 0.900 J/g °C
- ΔT= 52 °C - 21°C= 31°C
Substitute these values into the formula.
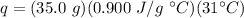
Multiply the first two values. The grams will cancel each other out.
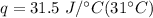
Multiply again. This time, the degrees Celsius cancel each other out, so the final units are Joules.
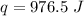
976.5 Joules of energy were required to heat the piece of metal.