Answer:
794 mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
We are going to be using the Combined Gas Law for this problem as well. Just to refresh out memory - the Combined Gas Law expresses the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature (in KELVIN) of a fixed amount of gas. The equation itself? Right here:
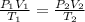
Now, looking at the problem, let's assign the values to its corresponding variable:
P1 = 800mmHg; V1 = 5.0L; T1 = -50°C + 273 = 223K
V2 = 7.0L; T2 = 37°C + 273 = 310K; P2 = ?
We are looking to find the new pressure, a.k.a. P2. So, let's plug and chug the values into the equation.
Set up:
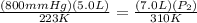
==>
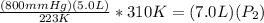
==>
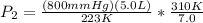
==>
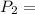 794.36 = 794 mmHg
794.36 = 794 mmHg