Answer:
There are two possible options:
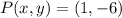 or
or
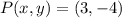 .
.
Explanation:
There are two possible options depending on what the point of origin is. Vectorially speaking, we can determine the coordinates of the point that partitions the segment is described below:
![P(x,y) = A(x,y) + r\cdot [B(x,y) - A(x,y)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/psabti32hkpxe5awthy67p6bicedwi9xh1.png) (1)
(1)
Where:
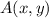 - Point of origin.
- Point of origin.
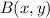 - Point of destination.
- Point of destination.
 - Partition factor.
- Partition factor.
Option 1:
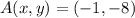 ,
,
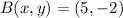 ,
,
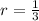
![P(x,y) = (-1, - 8) + (1)/(3)\cdot [(5,-2)-(-1,-8)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/fqyq9ffkclopbvpq4k25693y74qd5qrnt9.png)

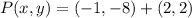
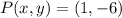
Option 2:
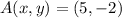 ,
,
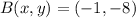 ,
,
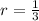
![P(x,y) = (5,-2) + (1)/(3)\cdot [(-1,-8)-(5,-2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/x4vgi063nv7f4ep15wha5fun5z3cua076l.png)
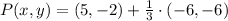
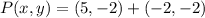
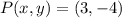
There are two possible options:
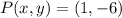 or
or
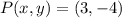 .
.