Answer:
the magnetic field experienced by the electron is 0.0511 T
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the data in the question;
Wavelength λ = 21 cm = 0.21 m
we know that Bohr magneton μ
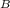 is 9.27 × 10⁻²⁴ J/T
is 9.27 × 10⁻²⁴ J/T
Plank's constant h is 6.626 × 10⁻³⁴ J.s
speed of light c = 3 × 10⁸ m/s
protein spin causes magnetic field in hydrogen atom.
so
Initial potential energy = -μ
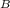 B × cos0°
B × cos0°
= -μ
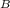 B × 1
B × 1
= -μ
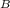 B
B
Final potential energy = -μ
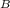 B × cos180°
B × cos180°
= -μ
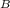 B × -1
B × -1
= μ
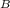 B
B
so change in energy will be;
ΔE = μ
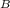 B - ( -μ
B - ( -μ
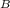 B )
B )
ΔE = 2μ
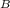 B
B
now, difference in energy levels will be;
ΔE = hc/λ
2μ
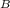 B = hc/λ
B = hc/λ
2μ
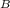 Bλ = hc
Bλ = hc
B = hc / 2μ
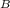 λ
λ
so we substitute
B = [(6.626 × 10⁻³⁴) × (3 × 10⁸)] / [2(9.27 × 10⁻²⁴) × 0.21 ]
B = [ 1.9878 × 10⁻²⁵ ] / [ 3.8934 × 10⁻²⁴ ]
B = 510556326.09
B = 0.0511 T
Therefore, the magnetic field experienced by the electron is 0.0511 T