Answer:
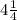
Explanation:
The fraction of bushels of tomatoes that Tony picked up = 5
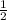
The fraction of bushels that he gave to his grandmother = 1
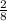
The fraction of bushels he sold =?
To find the answer for the above, you have to subtract the fraction of bushels of tomatoes he gave by the fraction of bushels of tomatoes that he picked.
Let us solve.
The fraction of bushels of tomatoes he sold :
5
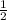 - 1
- 1
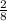
First, make both the above improper fractions.

To make the denominators of the fractions common, multiply both sides of 11/2 by 4.
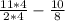

Now subtract the fractions.
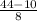
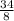
Now to write the fraction in its simplest form divide both sides by 2.
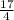
Now make the answer a mixed number.
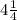
Therefore,
Tony sold
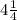 bushels of tomatoes
bushels of tomatoes