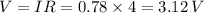Step-by-step explanation:
First Calculate Total Equivalent Resistance (Series) :
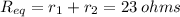
(A) Current in each resistor :
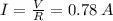
(Since this is a series connection, the electric current is same through both resistor).
(B) Potential Difference across the first resistor :
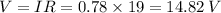
(B) Potential Difference across the second resistor :