Answer:
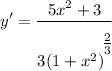
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Algebra I
- Functions
- Function Notation
- Exponential Rule [Root Rewrite]:
![\displaystyle \sqrt[n]{x} = x^{(1)/(n)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/yqpyvbuov0tgbjo8vla0qsqp67pafn2fr7.png)
Algebra II
- Logarithms and Natural Logs
- Logarithmic Property [Multiplying]:
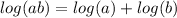
- Logarithmic Property [Exponential]:
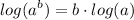
Calculus
Derivatives
Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/rwpyhrof52dro5d128gleq5obchnuu5qkj.png)
Derivative Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(x) + g(x)] = (d)/(dx)[f(x)] + (d)/(dx)[g(x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/i90hl6t3gcguvrecodn8t9gnodav0w5ns8.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Derivative Rule [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(g(x))] =f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/vue68srn3fe6bds4idxorm97z7tgwelamw.png)
Logarithmic Derivative:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [lnu] = (u')/(u)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/zf0m3fv68j30cbn0bslnu5admdwd4laga9.png)
Implicit Differentiation
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
![\displaystyle y = x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/vfzc6wiyigbrfndu0ehnvpht71939h9hic.png)
Step 2: Rewrite
- [Equality Property] ln both sides:
![\displaystyle lny = ln(x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2})](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/whlnmwrpwtwp39mfe9vw243d6jtd2vhbct.png)
- Logarithmic Property [Multiplying]:
![\displaystyle lny = ln(x) + ln(\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2})](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/ht7nt5cb56e5ttvres8af5qymzuv3h0gqq.png)
- Exponential Rule [Root Rewrite]:
![\displaystyle lny = ln(x) + ln \bigg[ (1 + x^2)^\bigg{(1)/(3)} \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/cl6625psuchjg0mzj1vcqo050atbeq0um6.png)
- Logarithmic Property [Exponential]:
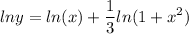
Step 3: Differentiate
- ln Derivative [Implicit Differentiation]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[lny] = (d)/(dx) \bigg[ ln(x) + (1)/(3)ln(1 + x^2) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/ihsnyf31svtcvfekej1bpz3f7dsmdaj2s9.png)
- Rewrite [Derivative Property - Addition]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[lny] = (d)/(dx)[ln(x)] + (d)/(dx) \bigg[ (1)/(3)ln(1 + x^2) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/3fwakhxy65y8lu91vyd7y0fdqkufgxap8c.png)
- Rewrite [Derivative Property - Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[lny] = (d)/(dx)[ln(x)] + (1)/(3)(d)/(dx)[ln(1 + x^2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/ders4tykco46po40xopv19q7b9ou58d6ax.png)
- ln Derivative [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (y')/(y) = (1)/(x) + (1)/(3) \bigg( (1)/(1 + x^2) \bigg) \cdot (d)/(dx)[(1 + x^2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/kn5gfpj9co0gu1ei6eubr09sb6jt84cd94.png)
- Rewrite [Derivative Property - Addition]:
![\displaystyle (y')/(y) = (1)/(x) + (1)/(3) \bigg( (1)/(1 + x^2) \bigg) \cdot \bigg( (d)/(dx)[1] + (d)/(dx)[x^2] \bigg)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/f1tlg0mgf1uiq0f8f5vph082waw17u9f5w.png)
- Basic Power Rule]:
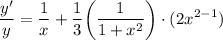
- Simplify:
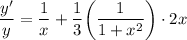
- Multiply:
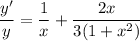
- [Multiplication Property of Equality] Isolate y':
![\displaystyle y' = y \bigg[ (1)/(x) + (2x)/(3(1 + x^2)) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/eutff98tj0fqzaqffvlx3sx8d0d2d5lgyu.png)
- Substitute in y:
![\displaystyle y' = x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2} \bigg[ (1)/(x) + (2x)/(3(1 + x^2)) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/9k8mj8coe641t96tqteddq1hd9a5mxgdwg.png)
- [Brackets] Add:
![\displaystyle y' = x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2} \bigg[ (5x^2 + 3)/(3x(1 + x^2)) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/5qxdkaryq9f93yqy1lp54kg56wo4ez1gea.png)
- Multiply:
![\displaystyle y' = \frac{(5x^2 + 3)\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2}}{3(1 + x^2)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/b38ynjkpsei1f9rna19azgyf6mi1fi3f1b.png)
- Simplify [Exponential Rule - Root Rewrite]:
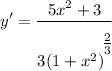
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Implicit Differentiation
Book: College Calculus 10e