Answer:
B. Ksp = 1.7 × 10¯⁷
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, for this solubility equilibrium problem, we first need to set up the chemical reaction describing the dissolution of the involved salt, CuCl:
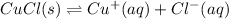
Next, we write the corresponding equilibrium expression:
![Ksp=[Cu^+][Cl^-]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/1x49dh1m5kylvhghd5nf7ex3jkdfnslqyu.png)
Now, we need to calculate the concentrations of copper (I) and chloride ions at equilibrium; thus, given that 0.041 g of this solid is completely dissolved in 1.0 L of solution, we can firstly calculate the moles present in the solution:
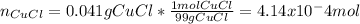
Afterwards, since all the species in the reaction, CuCl, Cu+ and Cl- are in a 1:1:1 mole ratio, we realize that those moles correspond to ions in the solution, so their concentrations are:
![[Cu^+]=[Cl^-]=(4.14x10^(-4)mol)/(1.0L)= 4.14x10^(-4)M](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/yfczbksnxial9957j7jf7p21mb0kl25zmf.png)
Then, we compute the Ksp by plug this value in the equilibrium expression:
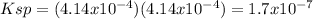
Thus, the answer would be B. Ksp = 1.7 × 10¯⁷.
Regards!