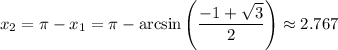Answer:
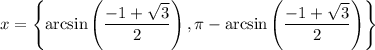
Or their approximations:
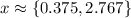
Explanation:
We are given:
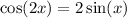
And we want to find the solution in [0, 2π).
Recall the double-angle identities for cosine:
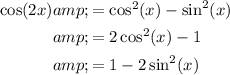
We will use the third version. Hence:
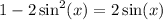
Move all terms to one side:
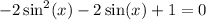
This is now in quadratic form. For simplicity, let u = sin(x):
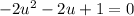
Solve for u. Simplify:
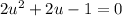
By the quadratic formula:
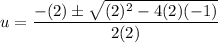
Evaluate:
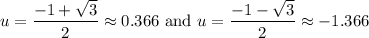
Note that the second solution is > -1. Hence, we will disregard it. (The range of sine is only -1 ≤ y ≤ 1.)
Back-substitute:
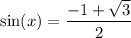
Since it is approximately 0.366, it will occur twice (once in QI and again in QII. This is because sine is positive only in those two quadrants). Using a calculator:
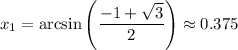
Using reference angles, the other solution is: