Answer:
The total amount of energy required is 25,515.2 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
Calorimetry is the measurement and calculation of the amounts of heat exchanged by a body or a system.
When a system absorbs (or gives up) a certain amount of heat, it can happen that:
- experience a change in its temperature, which involves sensible heat,
- undergoes a phase change at constant temperature, or latent heat.
To calculate the latent heat the formula is used:
Q = m. L
Where
- Q: amount of heat
- m: mass
- L: latent heat
To calculate sensible heat the following formula is used:
Q = m. c. ΔT
where:
- Q: amount of sensible heat
- m: body mass
- c: specific heat of the substance
- ΔT: temperature range
In this case, you have in the first place a heat to raise the temp of the water from 35.0 C to 100 C, where the specific heat value for water is 4.184
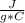 :
:
q1 = m*c*(Tfinal-Tinitial)
q1 = 10.0 g *(4.184
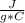 )* (100 - 35.0 C) = 2719.6 J
)* (100 - 35.0 C) = 2719.6 J
Now you have the heat to vaporize the water, where the heat of vaporization is 2259.36
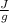 :
:
q2 = m*(heat of vaporization)
q2 = 10.0 g*(2259.36
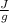 ) = 22593.6 J
) = 22593.6 J
Finally, you have the heat to raise temp of steam to 110 C, where the specific heat value for steam is 2.02
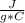 :
:
q3 = m*c*(Tfinal-Tinitial)
q3 = 10.0 g*(2.02
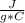 )*(110-100 C) = 202 J
)*(110-100 C) = 202 J
The total amount of energy can be calculated as:
Q= q1 + q2 + q3
Q= 2719.6 J + 22593.6 J + 202 J
Q=25,515.2 J
The total amount of energy required is 25,515.2 J.