Answer:
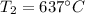
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, considering this problem as pressure constant, since the change is exhibited in temperature and volume only, it is possible for us to use the Charles' law as shown below:
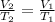
Thus, by solving for the final temperature, we obtain:
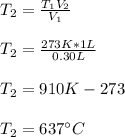
Best regards!