Solution :
a).
Given : Number of times, n = 25
Sigma, σ = 0.200 kg
Weight, μ = 13 kg
Therefore the hypothesis should be tested are :
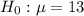
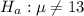
b). When the value of
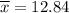
Test statics :
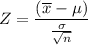
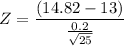
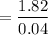
= 45.5
P-value = 2 x P(Z > 45.5)
= 2 x 1 -P (Z < 45.5) = 0
Reject the null hypothesis if P value < α = 0.01 level of significance.
So reject the null hypothesis.
Therefore, we conclude that the true mean measured weight differs from 13 kg.