Answer:
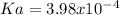
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, since the modelling of titration problems can be approached via the Henderson-Hasselbach equation to set up a relationship between pH, pKa and the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base, we can write:
![pH=pKa+log(([NO_2^-])/([HNO_2]) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/15slb5cs24f1z7shdtheay6dnq8odpfb90.png)
Whereas the pH is given as 3.14 and the concentrations are the same, that is why the pH would be equal to the pKa as the logarithm gets 0 (log(1)=0); thus, we can calculate the Ka via:
Best regards!