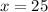Answer:
see below
Explanation:
Question-6:
we are given a equation
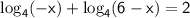
to solve so
recall logarithm multiplication law:
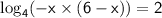
simplify multiplication:
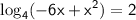
remember
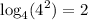
so
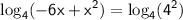
cancel out
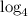 from both sides:
from both sides:
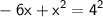
simplify squares:
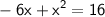
move left hand side expression to right hand side and change its sign:
since we are moving left hand side expression to right hand side there'll be only 0 left in the left hand side
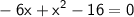
rewrite it to standard form i.e ax²+bx+c=0

rewrite -6x as 2x-8x:
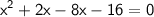
factor out x and 8:
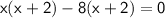
group:
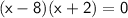
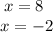
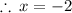
Question-7:
move left hand side log to right hand side:
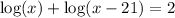
use mutilation logarithm rule;
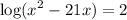
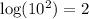 so
so
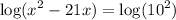
cancel out log from both sides:
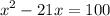
make it standard form:
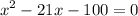
factor:
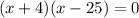
so