Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical equation of this reaction;
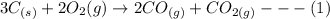
Using the Stochiometric ratio of ratio; the product formed will be aligned with the stoichiometric ratio limiting reagent.
Thus, 3 moles of C yields 1 mole of
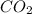 and 2 moles of CO.
and 2 moles of CO.
Therefore;
1 mole of C yields 1/3 moles of
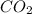 and 2/3 moles of CO
and 2/3 moles of CO
0.147 moles of C yields
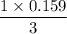 moles of
moles of
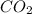 and
and
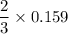 moles of CO
moles of CO
= 0.053 moles of
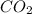 and 0.106 moles of CO
and 0.106 moles of CO
Also;
From the above reaction;
3 moles C reacts with 2 moles of
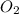
1 mole of C reacts with
 moles of
moles of
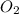
0.159 moles of C react with
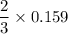 moles of
moles of
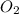
= 0.106 moles of
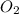
The remaining amount of
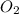 = (0.117 - 0.106) mol
= (0.117 - 0.106) mol
= 0.011 mol
The mixture comprises of the following after the reaction;
= 0.011 mol excess
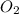 + 0.053 moles of
+ 0.053 moles of
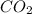 + 0.106 mol CO
+ 0.106 mol CO
= 0.17 moles of gas
Thus; moles fraction of CO is;
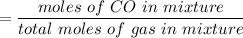
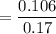
= 0.624